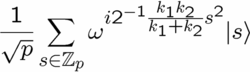Difference between revisions of "Research:The Hidden Subgroup Problem"
(New page: What new computational tasks can quantum computers perform more efficiently than their classical bretheren? This question is extremely ambitious and is perhaps one which is too big for any...) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
What new computational tasks can quantum computers perform more efficiently than their classical bretheren? This question is extremely ambitious and is perhaps one which is too big for anyone to ever fully answer. At the same time there is a great need to find new algorithms where quantum computer outperform classical computers. We are interested in finding these new algorithms. | What new computational tasks can quantum computers perform more efficiently than their classical bretheren? This question is extremely ambitious and is perhaps one which is too big for anyone to ever fully answer. At the same time there is a great need to find new algorithms where quantum computer outperform classical computers. We are interested in finding these new algorithms. | ||
| + | [[Image:Hs.png|right|thumb|250px|A hidden subgroup state]] | ||
We have focused our initial investigations into new quantum algorithms in the area of nonabelian hidden subgroup problems. An ongoing project focuses on extracting out the crux of why certain nonabelian hidden subgroup problems are efficiently solvable. Efficient quantum algorithms for these problems are important as they could lead to efficient quantum algorithms for graph isomorphism and certain unique-k-shortest vector in a lattice problems. | We have focused our initial investigations into new quantum algorithms in the area of nonabelian hidden subgroup problems. An ongoing project focuses on extracting out the crux of why certain nonabelian hidden subgroup problems are efficiently solvable. Efficient quantum algorithms for these problems are important as they could lead to efficient quantum algorithms for graph isomorphism and certain unique-k-shortest vector in a lattice problems. | ||
Revision as of 01:41, 4 February 2008
What new computational tasks can quantum computers perform more efficiently than their classical bretheren? This question is extremely ambitious and is perhaps one which is too big for anyone to ever fully answer. At the same time there is a great need to find new algorithms where quantum computer outperform classical computers. We are interested in finding these new algorithms.
We have focused our initial investigations into new quantum algorithms in the area of nonabelian hidden subgroup problems. An ongoing project focuses on extracting out the crux of why certain nonabelian hidden subgroup problems are efficiently solvable. Efficient quantum algorithms for these problems are important as they could lead to efficient quantum algorithms for graph isomorphism and certain unique-k-shortest vector in a lattice problems.